Computer Models
|
|
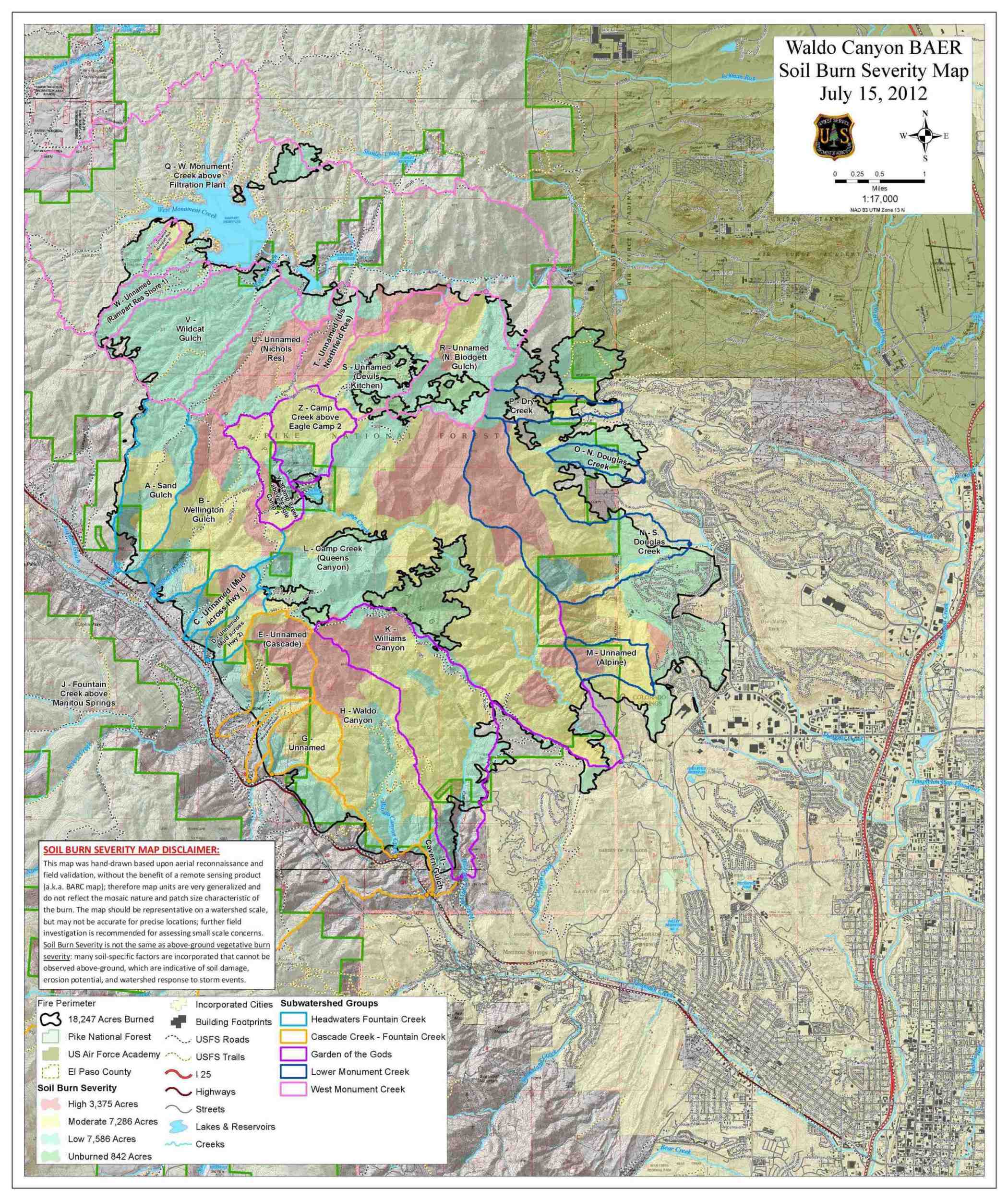
A soil burn severity map produced by a BAER team following the Waldo Canyon Fire. |
The size and probability of some threats occurring can be predicted using various computer models. Below are models commonly used by BAER teams that are also available for use by teams from state agencies and those helping private landowners and communities.
These models have a wide range in terms of their ease-of-use, accessibility, and required input or skills. Particularly user friendly models are identified with asterisks (*) and methods that require no expertise from the user are identified with double asterisks (**). The models are listed by how often they are used.
Erosion Risk Management Tool (ERMiT)*
The ERMiT is a web-based application that uses Water Erosion Prediction Project (WEPP) technology to estimate erosion, in probabilistic terms, on burned and recovering forest, range, and chaparral lands with and without the application of erosion mitigation treatments. This tool was developed to help land managers and decision-makers choose where, when, and how to apply the most effective post-fire mitigation treatments. For more information on how to use ERMiT, please see the ERMiT User Manual.
Disturbed WEPP Model*
Disturbed WEPP is an interface to the Water Erosion Prediction Project soil erosion model that allows users to easily describe numerous disturbed forest and rangeland erosion conditions. The interface presents the results as a summary and extended WEPP outputs, and also presents the probability of a given level of erosion occurring the year following a disturbance. For more information on how to use Disturbed WEPP, please see the Disturbed WEPP Technical Documentation.
AGWA
The Automated Geospatial Watershed Assessment (AGWA) tool is a GIS-based hydrologic model that uses commonly available GIS data layers to parameterize, execute, and spatially visualize results from watershed runoff and erosion models. Accommodating novice to expert GIS users, it is designed to be used by watershed, water resource, land use, and resource managers and scientists investigating the hydrologic impacts of land-cover/land-use change in small watershed to basin-scale studies.
Wildcat5
Wildcat5 is an interactive Windows Excel®-based software package designed to assist watershed specialists in analyzing rainfall runoff events to predict peak flow and runoff volumes generated by single-event rainstorms for a variety of watershed soil and vegetation conditions. It is a user-friendly, touch-and-feel, follow-your-nose program usable by anyone who has experience in Excel and some background in the fundamentals of rainfall-runoff models. To these users, most of it should be self-explanatory and intuitively obvious. The program offers extensive help options that provide guidance for the large number of input options and the most commonly used options are generally highlighted as defaults. For more information on how to use Wildcat5, please see the Wildcat5 User Manual.
Emergency Assessment of Post-Fire Debris-Flow Hazards**
Wildfire can significantly alter the hydrologic response of a watershed to the extent that even modest rainstorms can produce dangerous flash floods and debris flows. The USGS uses geospatial data related to basin morphometry, burn severity, soil properties, and rainfall characteristics to estimate the probability and volume of debris flows that may occur in response to a design storm. Post-fire debris-flow hazard assessments for recently burned areas in the western United States are provided free to any interested Federal, State, or Local Agency, or to any private organization, company, or individual. Requests for assessments or questions can be directed to Dennis Staley or Jason Kean.
FIRE HYDRO
Fire Hydro is an Excel spreadsheet which computes watershed curve numbers for four conditions: 1) pre-fire, 2) early post-fire with possible hydrophobicity, 3) medium term post-fire with hydrophobicity no longer in effect, but little re-emergent vegetation, and 4) later post-fire, after one growing season. This modelâs intended use is for engineers and technicians with hydrology experience to be able to quickly analyze the hydrology of watersheds that have recently experienced a fire. For more information on how to use FIRE HYDRO, please see the Fire Hydro User Notes.
VAR Calculation Tool*
The Values-at-risk (VAR) calculation tool is an Excel spreadsheet that can be used to calculate the benefit to cost ratio of various treatments, as well as the implied minimum value of the identified VAR. Furthermore, it can help BAER teams organize and summarize the justification for recommended treatment expenditures. For more information, see Assessing Post-Fire Values-at-Risk With a New Calculation Tool.
Forest Service Peak Flow Calculator*
The FS Peak Flow Calculator estimates peak flow for burned areas using Curve Number methods. It is a simple web interface and requires the user to run ERMiT to obtain inputs for the Peak Flow Calculator. For more information on how to use ERMiT and the Peak Flow Calculator, please see Instructions from the Forest Service.
FERGI Model
The Fire-Enhanced Runoff and Gully Initiation Model (FERGI) is a post-fire, erosion prediction utility that can help users estimate the likelihood of runoff generation amounts and gully initiation positions on hillslopes after fire and after treatments. FERGI reports return intervals for runoff generation rates and totals, how high up the hillslope gullies will initiate, and the changes that might be expected with mitigation. For more information or to access the FERGI model, please contact Charlie Luce or Sharon Parkes.
RUSLE2
The Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation 2 (RUSLE2) is a computer program that estimates rates of rill and interrill soil erosion caused by rainfall and its associated overland flow. The user applies RUSLE2 to a specific site by describing field conditions at the site for climate, soil, topography, and landuse. For more information on how to use RUSLE2, please see the User's Guide.
StreamStats
The StreamStats program was produced by the USGS as a web application that incorporates GIS to provide users with access to an assortment of analytical tools that are useful for water resource planning and engineering. Users can select USGS data-collection station locations shown on a map and obtain previously published information for the stations, including descriptive information, and previously published basin characteristics and streamflow statistics. For more information on how to use StreamStats, please see these User Instructions.
WinTR-55
WinTR-55 is a single-event rainfall-runoff, small watershed hydrologic model. It generates hydrographs from both urban and agricultural areas and at selected points along the stream system. Hydrographs are routed downstream through channels and/or reservoirs. Multiple sub-areas can be modeled within the watershed. For more information on how to use WinTR-55, please see the WinTR-55 User Manual.
USGS Regression Equations
The National Streamflow Statistics Program is a computer program that should be useful to engineers, hydrologists, and others for planning, management, and design applications. NSS compiles all current USGS regional regression equations for estimating magnitude and frequency of floods at both gaged and ungaged streams in an easy-to-use interface. For more information on how to use the National Streamflow Statistics Program, please see this USGS Report.
HEC-HMS
The Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS) was produces by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to simulate precipitation-runoff processes of dendritic drainage basins. It can be used in many different geographic areas to produce hydrographs that are used to determine rainfall hydrographs in burned landscapes.